Key Takeaways:
-
Swelling after surgery is a common part of the body’s healing process, caused by inflammation, reduced movement, certain medications, and individual health factors. While normal, too much swelling can cause discomfort and delay recovery, so understanding its causes is the first step toward managing it effectively.
-
Managing swelling is important for improving comfort, protecting healing tissues, and helping restore mobility, especially after surgeries involving joints or high-impact areas.
-
Other helpful strategies include elevating the affected area, applying ice, staying hydrated, eating well, and gently moving as advised by a healthcare provider. If swelling worsens or is paired with symptoms like redness, fever, or increased pain, medical attention is needed to rule out complications and ensure safe recovery.
Experiencing some degree of swelling, or edema, is a common occurrence after surgery. This is your body's natural response to an invasive procedure and is a part of the healing process. However, excessive swelling can lead to discomfort and prolong the recovery period.
Here, we’ll explore what causes swelling after surgery, the importance of managing it effectively, and how to support your post-surgical recovery.
What Causes Swelling After Surgery?
Swelling after surgery, also known as postoperative edema, primarily occurs due to the body's inflammatory response to the surgical procedure. When your body undergoes surgery, it responds by sending fluid and white blood cells to the affected area to kickstart the healing process.
This influx of fluid can cause the area to swell, leading to a noticeable increase in size and a feeling of tightness or discomfort. The type of surgery can also have a significant impact on the degree of swelling.
Surgeries that involve significant tissue disruption or are performed on weight-bearing joints like the knee or hip often result in more noticeable swelling. This is because these areas are subjected to a greater amount of stress and pressure, leading to a more pronounced inflammatory response.
Other Factors
Certain medications administered during and after surgery can also contribute to swelling. Pain relievers and anesthetics, for example, can cause fluid retention in some individuals. This is because these medications can alter the balance of fluids and electrolytes in your body, leading to an accumulation of fluid in certain areas.
Reduced physical activity following surgery can also lead to swelling. When you're inactive, your circulatory system doesn't get the usual help from muscle contractions to move fluid back up toward the heart.
As a result, fluid can accumulate in the lower extremities, causing swelling. This is particularly common after surgeries involving the legs or hips, where mobility may be significantly limited during the initial recovery period.
Lastly, individual factors can also influence post-surgical swelling. These include your overall health status, age, and whether you have any underlying conditions that could affect fluid balance, such as kidney disease or heart failure.
Understanding the causes of post-surgical swelling is the first step toward managing it effectively.
Why Is Managing Swelling Important?
Effectively managing post-surgical swelling is crucial for several reasons:
- Firstly, it can significantly enhance your comfort levels during recovery. Excessive swelling can lead to tightness and discomfort around the surgical area, making movement challenging and restful sleep elusive.
- Secondly, managing swelling can potentially speed up your recovery process. While some degree of swelling is normal and necessary for healing, excessive swelling can put added pressure on surrounding tissues and impede the healing process.
- Finally, controlling swelling can help improve mobility and function faster after surgery. This is particularly important after orthopedic surgeries, where regaining range of motion is a critical part of the rehabilitation process.
As such, while swelling is a normal part of the post-surgery landscape, it's crucial to manage it effectively to provide a smooth, comfortable, and speedy recovery.
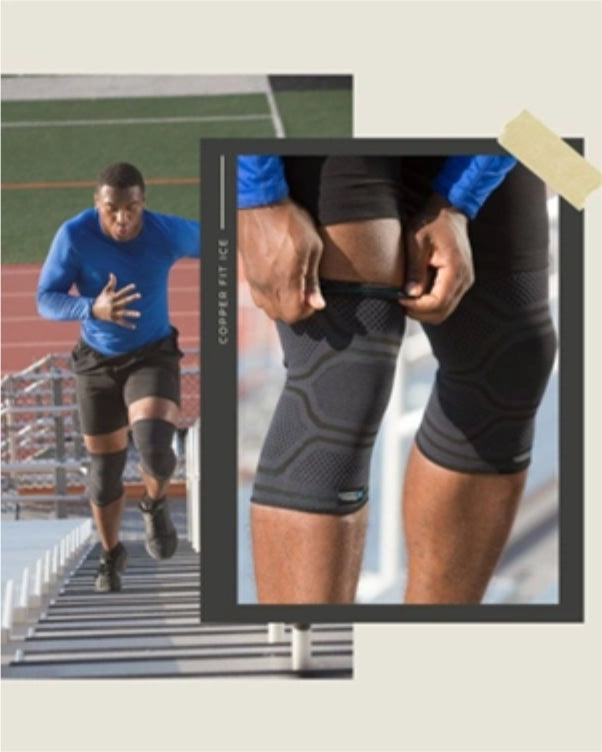
What Role Does Compression Play in Managing Swelling?
Compression plays a supportive role in managing post-surgical swelling. It applies gentle, consistent pressure to the affected area, which can help maintain the normal fluid balance in the tissues.
When you wear a compression garment, it exerts pressure on the tissue underneath and supports the function of your lymphatic system, a network of vessels and nodes in your body that removes waste products.
Compression garments come in various forms, including socks, sleeves, and wraps, and can be used on different parts of the body, depending on where the swelling is located.
What Other Methods Can Help Manage Swelling After Surgery?
While compression support can play a role in managing post-surgical swelling, other strategies can also be beneficial and are often recommended by healthcare professionals.
- Elevation: Elevating the affected area above the level of your heart can help reduce swelling. This technique utilizes gravity to encourage fluid to flow away from the swollen area and back towards the heart. It's a simple yet effective strategy that can be done several times a day.
- Ice Application: Applying cold packs to the swollen area can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing relief from discomfort. Always wrap the ice pack in a cloth to protect your skin, and follow your healthcare provider's advice on how often and how long to apply the ice.
- Gentle Movement: While rest is essential after surgery, so is gentle movement. Depending on your doctor's advice, gentle exercises can help stimulate blood flow and reduce fluid accumulation. This can be as simple as performing ankle circles or going for short, slow walks, depending on the area of surgery.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Staying well-hydrated and eating a balanced diet rich in protein can also support your recovery and help manage swelling. Proper hydration can help your body flush out excess fluid, while protein can aid in tissue repair and recovery.
- Medication: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medication to help control swelling. Always take medication as directed by your healthcare provider. Don't hesitate to ask them any questions you might have about the medication's purpose or potential side effects.
Each person's recovery is particular to them. What works for one person might not work for another. It's important to listen to your body and follow your healthcare provider's advice. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific surgery, overall health, and recovery progress.
When Should You Seek Medical Attention for Post-Surgical Swelling?
While some degree of swelling after surgery is expected, it's important to carefully monitor your recovery and seek medical attention if the swelling becomes excessive or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Signs that you should consult your healthcare provider include swelling that continues to worsen after several days, redness, warmth, or tenderness around the surgical area, and fever or chills. Other alarming symptoms could be changes in the color or amount of drainage from the surgical site, severe or increasing pain, or difficulty moving the affected area.
Your healthcare provider is your best resource during your recovery. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific surgery and overall health.
Don't hesitate to reach out and ask questions if you're uncertain about your symptoms. The goal is to provide a smooth and healthy recovery; effective communication with your healthcare provider is key to achieving that.
FAQ
Does walking reduce swelling after surgery?
Yes, gentle walking can help reduce swelling after surgery. Movement, including walking, promotes blood circulation and helps the lymphatic system drain excess fluid, which can accumulate around the surgical site and cause swelling.
Is it better to walk or rest after surgery?
The short answer is both, but it's very important to start walking as soon as it's safe after your surgery. The sooner you start walking, the faster you will recover and go back to doing your normal activities.
What foods should you avoid during wound healing?
To support optimal wound healing, it's generally recommended to limit or avoid foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and processed ingredients. These can hinder the body's natural healing processes by increasing inflammation and potentially delaying tissue repair.
Making Sure Edema Doesn’t Get the Best of You
Managing swelling effectively is a vital part of the recovery process following surgery. While some degree of swelling is normal, excessive swelling can lead to discomfort and delay recovery.
Strategies such as using compression gear like Copper Fit products, elevating the affected area, applying ice, engaging in gentle movement, and maintaining good nutrition can all support the management of post-surgical swelling.
Always monitor your recovery closely, and don't hesitate to seek medical attention if swelling worsens or if other concerning symptoms arise. Your health and comfort are paramount, and taking proactive steps can help secure a smooth and speedy recovery.
Sources:
After Surgery: Discomforts and Complications | Johns Hopkins Medicine
What are Electrolytes? | Cedars-Sinai
RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) | UK Healthcare
Challenges and Solutions in Postoperative Complications: A Narrative Review in General Surgery - PMC





